Hydrogen is like a chameleon.
Depending on the situation, it can change colors. But not to camouflage, rather to show what it’s capable of.
And given its capabilities, hydrogen is quickly becoming a critical player in the global race toward decarbonization. For oil and gas executives, the push to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining profitability is more urgent than ever.
Hydrogen energy, with its potential to replace fossil fuels, is seen as a game-changer in this transition.
But here’s the catch: not all hydrogen is created equal.
There’s green hydrogen, produced from renewable energy, blue hydrogen, derived from natural gas with carbon capture, and grey hydrogen, the least sustainable option.
With so many types of hydrogen, many in the industry are left confused about how each fits into a broader decarbonization strategy.
Green, Blue, and Grey Hydrogen—What’s the Difference?
Can hydrogen truly be the key to a low-carbon future for the oil and gas sector? The answer depends on understanding its potential, and how the right type of hydrogen could drive the industry toward a sustainable, profitable future.
Hydrogen is classified into three main types—green, blue, and grey—each with different production methods and environmental impacts.
| Hydrogen Type | Production Method | Emissions | Cost |
| Green Hydrogen | Electrolysis using renewable energy (wind/solar) | Zero emissions (cleanest option) | Highest cost (due to renewable energy infrastructure) |
| Blue Hydrogen | Natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS) | Low emissions (due to CCS) | Moderate cost (due to CCS technology) |
| Grey Hydrogen | Natural gas without carbon capture | High emissions (most polluting) | Lowest cost (widely available and cheap) |
Which hydrogen type is right for your company’s decarbonization goals? The choice depends on your sustainability ambitions, available resources, and long-term energy strategy.
How Hydrogen Reduces Carbon Emissions in Oil & Gas
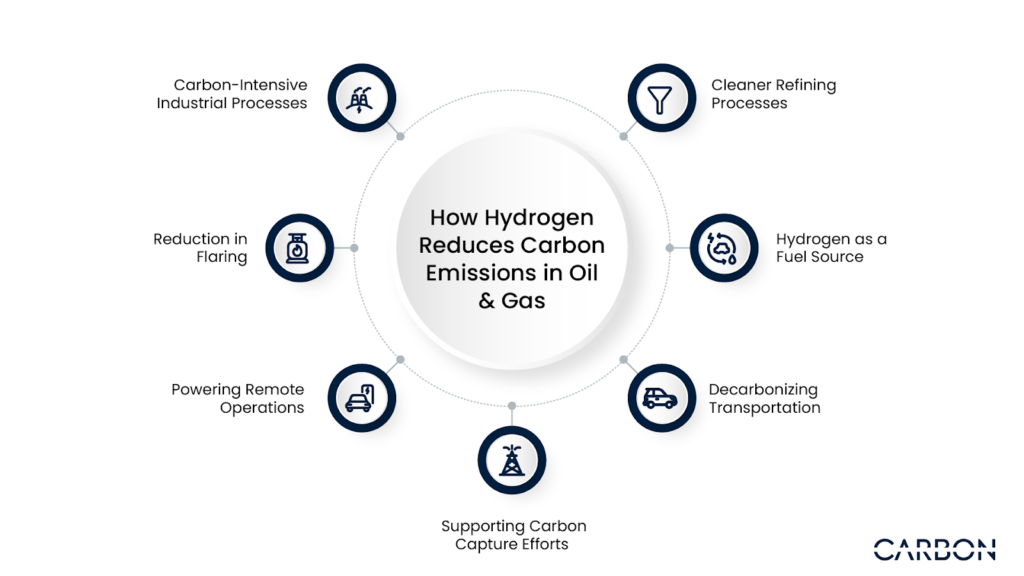
Hydrogen has emerged as a real solution for cutting down carbon emissions in oil and gas operations. By integrating hydrogen into key processes, oil and gas companies can significantly reduce carbon footprints while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Cleaner Refining Processes: Hydrogen is used in desulfurization, replacing traditional methods and reducing emissions from the refining process, especially in sulfur removal.
- Hydrogen as a Fuel Source: Hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel for heavy-duty vehicles and equipment, replacing diesel and other fossil fuels that produce higher carbon emissions.
- Decarbonizing Transportation: Hydrogen plays a role in the production of synthetic fuels and hydrogen-powered vehicles, helping to reduce emissions in transportation networks.
- Carbon-Intensive Industrial Processes: Industries like steel-making and chemical production can use hydrogen to replace natural gas, significantly lowering carbon emissions in these energy-intensive processes.
- Reduction in Flaring: By using hydrogen as an alternative energy source, companies can reduce or eliminate the need for flaring, which is a significant contributor to carbon emissions in oil and gas operations.
- Powering Remote Operations: Hydrogen can be used as a reliable energy source for remote oil and gas sites, eliminating the need for carbon-intensive diesel generators.
- Supporting Carbon Capture Efforts: Hydrogen can complement carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, reducing the overall emissions from natural gas and other fossil fuel-based operations.
Challenges of Producing and Integrating Hydrogen for Sustainable Energy Management
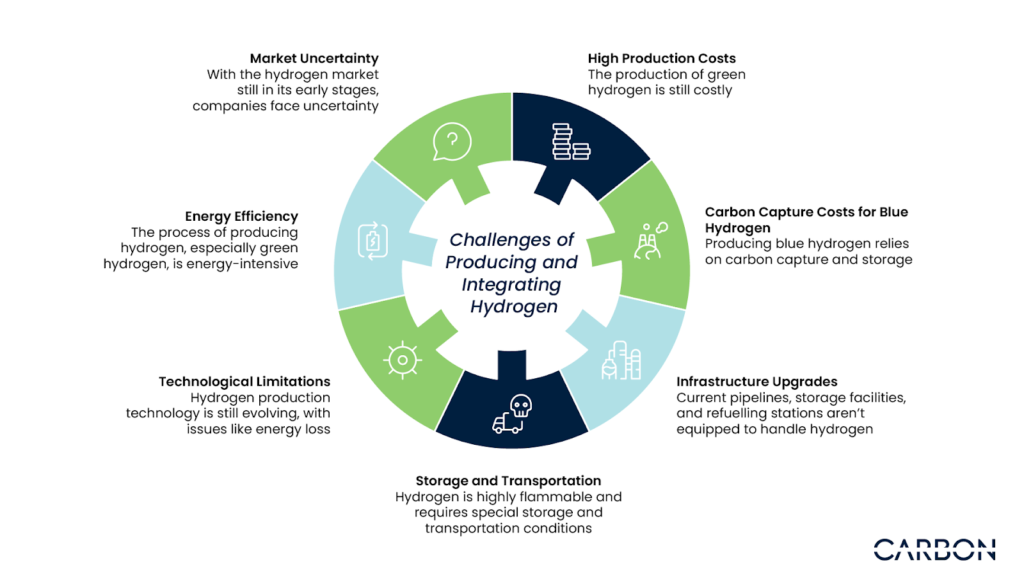
While hydrogen holds great potential for decarbonization, it doesn’t come without challenges. Producing and integrating hydrogen into existing oil and gas infrastructure requires significant investment and technological advancement.
1. High Production Costs
The production of green hydrogen is still costly due to the high expense of renewable energy infrastructure required for electrolysis.
2. Carbon Capture Costs for Blue Hydrogen
Producing blue hydrogen relies on carbon capture and storage (CCS), which adds a significant layer of cost, particularly in setting up the infrastructure to capture and store CO2.
3. Infrastructure Upgrades
Current pipelines, storage facilities, and refuelling stations aren’t equipped to handle hydrogen, meaning existing oil and gas infrastructure would require costly upgrades.
4. Storage and Transportation
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires special storage and transportation conditions, which increases logistical challenges and costs.
5. Technological Limitations
Hydrogen production technology is still evolving, with issues like energy loss during production and distribution limiting its efficiency.
6. Energy Efficiency
The process of producing hydrogen, especially green hydrogen, is energy-intensive, leading to questions about whether it’s always the most efficient decarbonization option.
7. Market Uncertainty
With the hydrogen market still in its early stages, companies face uncertainty regarding regulations, costs, and the future infrastructure needed to support widespread hydrogen use.
Hydrogen and the Global Energy Transition
As the world races toward decarbonization, hydrogen is emerging as a key player in global energy conversation and transition.
Countries around the world are investing heavily in hydrogen initiatives to meet sustainability goals and reduce their carbon footprints. From the European Union’s Hydrogen Strategy to Japan’s ambitious hydrogen energy plans, global efforts are underway to position hydrogen as a cornerstone of clean energy.
Meeting Regulatory Demands
As governments tighten emissions regulations, oil and gas companies face mounting pressure to find ways of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Global initiatives like the Paris Agreement and the EU’s Fit for 55 package are pushing industries toward net-zero targets, with hydrogen playing a critical role.
Countries like the U.S. are offering tax incentives for low-carbon hydrogen production, encouraging companies to transition from carbon-heavy fuels.
Integrating hydrogen energy helps meet these regulatory demands and ensures companies remain competitive in an evolving energy conservation landscape. Hydrogen is thus proving essential for compliance and long-term viability.
Hydrogen’s Role in Emissions Reduction
Hydrogen plays a key role in refining, replacing traditional methods used in desulfurization to lower sulfur emissions. In industrial processes like steelmaking, hydrogen can cut emissions by up to 30%.
In transportation, hydrogen fuel cells provide a cleaner alternative for heavy-duty vehicles, offering advantages over electric solutions for long-haul applications.
For many oil and gas executives, hydrogen is central to their decarbonization strategies, helping them reduce emissions while staying competitive in a low-carbon future.
Preparing for a Hydrogen-Powered Future
Consult with CarbonMinus for customized energy management strategies. Book a demo today at www.carbonminus.com and stay informed about the latest developments in your industry.
As regulations tighten and sustainability becomes non-negotiable, integrating new ideas into your energy strategy is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between green, blue, and grey hydrogen?
- Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy (wind, solar) to split water molecules, generating zero emissions.
- Blue hydrogen is produced from natural gas, but with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology to trap emissions.
- Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas without CCS, resulting in high carbon emissions.
2. How can hydrogen help oil and gas companies reduce their carbon emissions?
Hydrogen, especially green and blue hydrogen, can replace traditional fossil fuels in refining, transportation, and other carbon-intensive processes. By integrating hydrogen into operations, oil and gas companies can significantly cut CO2 emissions, helping them meet sustainability targets and regulatory requirements.
3. What are the challenges of producing and integrating hydrogen into oil and gas operations?
Key challenges include the high cost of producing green hydrogen, the need for infrastructure upgrades to store and transport hydrogen, and technological limitations related to scaling production. Hydrogen is also difficult to store, requiring specialized facilities, which can be expensive to implement.
4. How does hydrogen fit into the global energy transition?
Hydrogen is seen as a critical component of the global energy transition, helping industries achieve net-zero emissions by replacing fossil fuels with a cleaner, more sustainable energy source. Many countries are investing heavily in hydrogen as part of their sustainability goals, positioning it as a key solution for decarbonizing industries like oil and gas.




